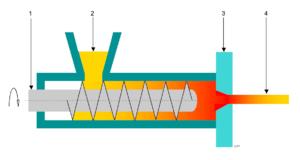
General principle
Extrusion is carried out using piston or screw extruders by feeding a plastic paste into the nozzle that determines the shape of the workpiece.
Detailed description
Extrusion is one of the existing ways to shape plastic paste. It is suitable for clay compositions (silicone ceramics), which are naturally plastic with a water content of between 15 and 25 %, or advanced ceramics, whose plasticity is provided by polymer additives (thermoplastic binders). The extruded plastic paste is from a press filter or a deaerating mixer. Piston extrusion is a discontinued process that offers a low dead volume, while vacuum screw pressing offers the productivity of a continuous process. The extruded material is cut to obtain parts in their final shape or blueprints which will be definitively formed by pressing or sizing.
Extrusion is used for the manufacture of perforated clay bricks, kiln-fired refractory bricks, bars or insulating tubes. This process is also used in the manufacture of porous membrane filters for the clarification, purification, separation and concentration of liquids, especially in harsh conditions. These membranes also allow the filtration of gases (particulate filters for cars, hot gas filters for industry) or molten metals.
Materials involved
Extrusion is commonly used with traditional ceramics such as cordierite, porcelain and mullite, and also with advanced ceramics in the alumina, zirconia and silicon carbide groups.
Advantages and disadvantages of this process
- Continuous process
- Long products
- Cost-saving process.
- Extrudable geometries
- Drying required.